Ever wondered what a lightning scar really is? Well, let me tell you, it's not just some random mark on a tree or a person—it's nature’s way of saying, "Hey, I was here!" Lightning scars are more than just physical marks; they’re stories of survival, resilience, and the raw power of nature. Whether it’s on a tree, rock, or even a human body, these scars leave an indelible reminder of the incredible forces at play in our world.
Now, before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let’s talk about why this topic matters. Lightning scars aren’t just cool to look at—they’re a testament to the incredible power of lightning and its impact on everything it touches. From trees that bear the brunt of a strike to humans who survive such encounters, there’s so much to learn about how lightning interacts with the world around us.
And here’s the kicker: understanding lightning scars isn’t just for scientists or nature enthusiasts. It’s something everyone should know about because, let’s face it, lightning is unpredictable and can strike anywhere. So, buckle up because we’re about to take a deep dive into the world of lightning scars, and trust me, it’s going to be a wild ride.
What Exactly Is a Lightning Scar?
A lightning scar, in its simplest form, is the mark left behind after a lightning strike. These scars can appear on trees, rocks, or even people, depending on where the lightning makes contact. For trees, the scar is often visible as a long, charred line running down the trunk. In humans, the scar might look like a strange, branched pattern resembling the shape of a lightning bolt.
But here’s the thing: not all lightning scars are created equal. Some are minor, leaving behind a faint mark, while others can be devastating, causing significant damage to whatever they touch. The severity of the scar depends on a variety of factors, including the intensity of the lightning strike, the material it hits, and the environment surrounding the strike.
So, what causes these scars? When lightning strikes, it generates an immense amount of heat—up to 50,000 degrees Fahrenheit! This heat can vaporize water inside trees, causing them to explode, or it can burn through skin, leaving behind a distinctive pattern. It’s nature’s way of showing just how powerful lightning really is.
How Do Lightning Scars Form on Trees?
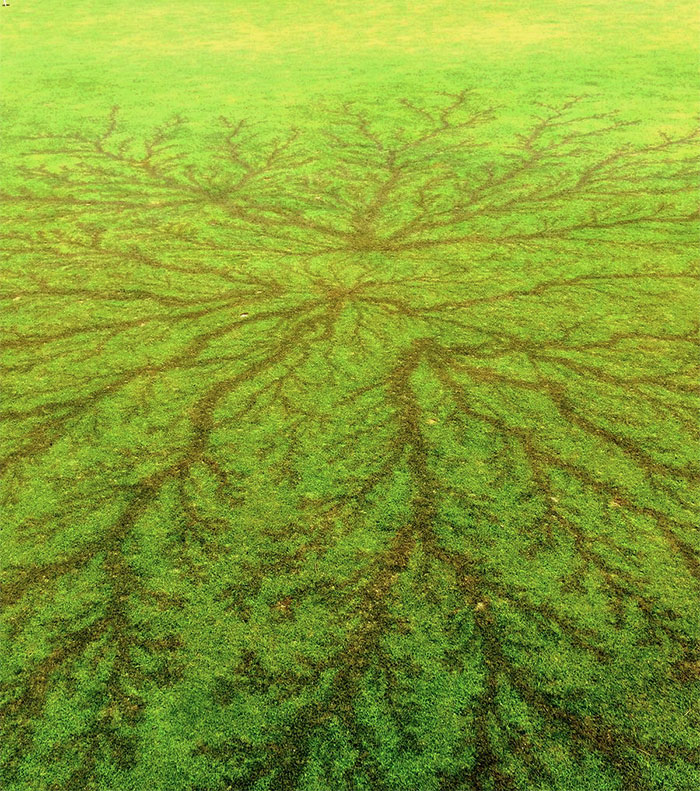
Trees are one of the most common victims of lightning strikes, and the scars they leave behind are often some of the most striking (pun intended). When lightning hits a tree, it typically travels along the outer layers of the trunk, where moisture is concentrated. This moisture turns into steam almost instantly, causing the bark to explode outward and leaving behind a deep, charred scar.
Some trees are more resilient than others when it comes to lightning strikes. For example, oak trees are often targeted by lightning due to their height and high water content, but they’re also more likely to survive the strike. On the other hand, pine trees, which have a higher resin content, tend to burn more easily and may not survive a direct hit.
Interestingly, some trees can live for years with a lightning scar, continuing to grow and thrive despite the damage. It’s a testament to their resilience and adaptability in the face of nature’s fury.
Lightning Scars on Humans: A Rare but Powerful Encounter
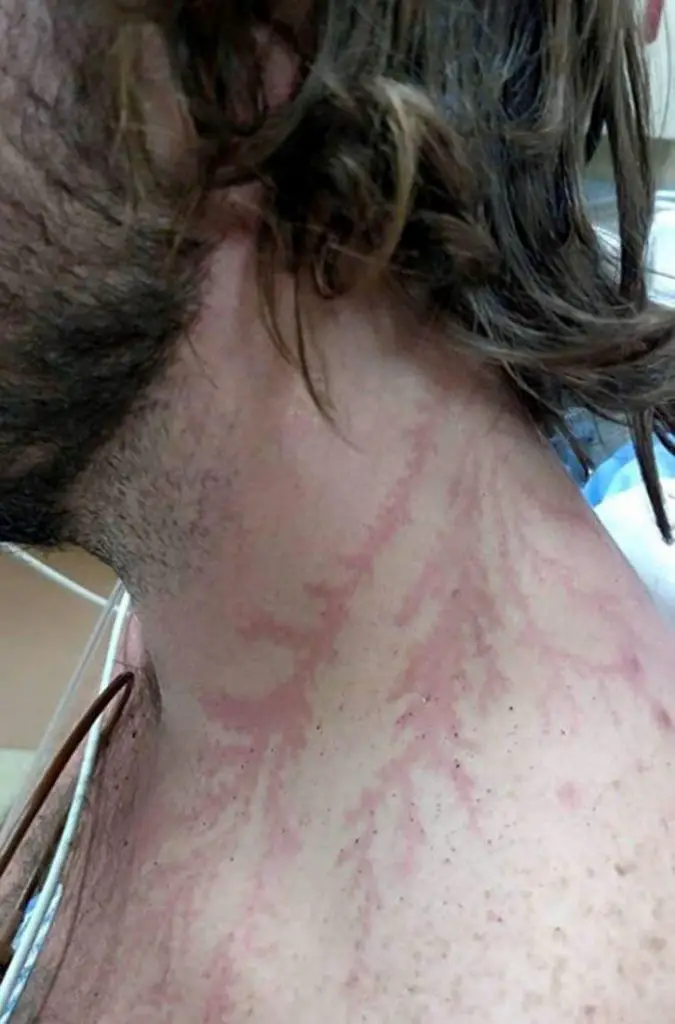
While lightning scars on trees are fascinating, the scars left on humans are even more intriguing—and often more terrifying. When lightning strikes a person, it can cause a range of injuries, from minor burns to severe internal damage. In some cases, the lightning can leave behind a distinctive pattern on the skin, known as a Lichtenberg figure.
A Lichtenberg figure is a branching, fern-like pattern that appears on the skin after a lightning strike. This pattern is caused by the electrical discharge traveling through the body, damaging the capillaries and leaving behind a visible mark. While these scars can be alarming, they’re also a reminder of the incredible power of lightning and the body’s ability to survive such an encounter.
It’s worth noting that not everyone who survives a lightning strike will develop a Lichtenberg figure. The appearance of the scar depends on a variety of factors, including the intensity of the strike, the location of the contact, and the individual’s physiology. Some people may only experience minor burns, while others may suffer from more serious injuries.
Surviving a Lightning Strike: Stories of Resilience
There are countless stories of people who have survived lightning strikes and lived to tell the tale. One such story is that of Roy Sullivan, a former park ranger who holds the Guinness World Record for being struck by lightning the most times—seven, to be exact. Despite his numerous encounters with lightning, Sullivan managed to survive each one, though not without some scars to show for it.
Another remarkable story is that of Mike Holmes, a storm chaser who was struck by lightning while filming a documentary. Holmes survived the strike with only minor injuries, but the experience left a lasting impression on him. He now uses his story to educate others about the dangers of lightning and the importance of staying safe during thunderstorms.
These stories of survival are a testament to the resilience of the human spirit and the body’s ability to withstand incredible forces. They also serve as a reminder of the importance of lightning safety and the need to respect the power of nature.
The Science Behind Lightning Scars
Now that we’ve covered the basics of what lightning scars are and how they form, let’s dive a little deeper into the science behind them. Lightning is an incredibly powerful force, capable of generating temperatures hotter than the surface of the sun. When it strikes, it releases an enormous amount of energy in a fraction of a second, leaving behind a lasting mark on whatever it touches.
But how exactly does lightning cause these scars? It all comes down to the electrical properties of the materials it interacts with. Trees, for example, are made up of water, cellulose, and other organic compounds. When lightning strikes a tree, the water inside is instantly vaporized, causing the bark to explode and leaving behind a charred scar. Similarly, when lightning strikes a person, it travels along the surface of the skin, damaging the capillaries and leaving behind a distinctive pattern.
Scientists have been studying lightning scars for years, trying to understand the mechanisms behind their formation. Through their research, they’ve discovered that the severity of the scar depends on a variety of factors, including the intensity of the strike, the moisture content of the material, and the surrounding environment. This knowledge is crucial for understanding the impact of lightning on the environment and developing strategies to mitigate its effects.
Factors That Influence Lightning Scar Formation
Not all lightning strikes result in scars, and not all scars are the same. Several factors influence the formation of lightning scars, including:
- Intensity of the Strike: The more powerful the strike, the more severe the scar.
- Material Composition: Trees with high water content are more likely to explode, while those with high resin content may burn more easily.
- Environmental Conditions: Moisture levels in the air and soil can affect the severity of the strike and the resulting scar.
- Location of Contact: The part of the tree or body that is struck can influence the appearance and severity of the scar.
Understanding these factors is essential for predicting the impact of lightning strikes and developing strategies to protect both people and property from their effects.
Preventing Lightning Scars: Safety Tips and Strategies
While lightning scars are fascinating, they’re also a reminder of the dangers of lightning. Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of being struck by lightning and minimize the chances of developing a scar.
First and foremost, always seek shelter during a thunderstorm. Avoid open fields, tall trees, and bodies of water, as these are all prime targets for lightning strikes. If you’re caught outside during a storm, try to find a low-lying area and crouch down with your feet together to minimize your exposure to the ground current.
Another important safety tip is to stay away from metal objects and electrical appliances during a storm. Lightning can travel through these objects, increasing your risk of being struck. If you’re indoors, avoid using the phone or taking a shower, as water pipes and phone lines can conduct electricity.
Finally, consider investing in a lightning protection system for your home or business. These systems are designed to safely direct lightning strikes away from your property, reducing the risk of damage and injury.
Lightning Protection Systems: How They Work
Lightning protection systems are an effective way to safeguard your property from the dangers of lightning. These systems typically consist of a series of components, including:
- Air Terminals: These are the tall, pointed rods that you often see on the roofs of buildings. They’re designed to intercept lightning strikes and direct the current safely to the ground.
- Down Conductors: These are the wires that connect the air terminals to the grounding system. They provide a safe path for the lightning current to travel.
- Grounding System: This is the final component of the system, designed to dissipate the lightning current safely into the ground.
By installing a lightning protection system, you can significantly reduce the risk of damage to your property and injury to yourself and your loved ones.
The Environmental Impact of Lightning Scars
Lightning scars aren’t just a concern for humans and property—they also have a significant impact on the environment. When lightning strikes a tree, it can cause significant damage to the surrounding ecosystem. The explosion of bark and wood can create openings for pests and diseases, making the tree more vulnerable to decay. In some cases, the tree may not survive the strike, leaving behind a dead or dying tree that can affect the balance of the ecosystem.
However, not all lightning scars are harmful. In some cases, they can actually benefit the ecosystem by creating habitats for wildlife. For example, the cavities left behind by lightning strikes can provide shelter for birds and other animals. Additionally, the charred wood can act as a natural fertilizer, enriching the soil and promoting new growth.
Understanding the environmental impact of lightning scars is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate their effects and protect the ecosystems they impact.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting Trees from Lightning Strikes
Conservationists are working hard to protect trees from the damaging effects of lightning strikes. One approach is to install lightning protection systems on valuable or historic trees, similar to those used on buildings. These systems are designed to intercept lightning strikes and direct the current safely to the ground, reducing the risk of damage to the tree.
Another approach is to plant trees in areas where they’re less likely to be struck by lightning. This might involve selecting species that are less attractive to lightning or planting them in areas with lower lightning activity. By taking these steps, conservationists can help ensure that our forests remain healthy and vibrant for generations to come.
Conclusion: Lightning Scars and Their Impact on Our World
In conclusion, lightning scars are more than just physical marks—they’re a testament to the incredible power of nature and the resilience of the world around us. Whether it’s a tree that survives a strike or a person who walks away with a Lichtenberg figure, these scars tell a story of survival and adaptation in the face of nature’s fury.
As we’ve learned, lightning scars can have a significant impact on both the environment and human lives. By understanding the science behind these scars and taking steps to mitigate their effects, we can better protect ourselves and the world around us from the dangers of lightning.
So, the next time you see a lightning scar, take a moment to appreciate the story it tells. And remember, if you’re ever caught in a thunderstorm, stay safe and respect the power of nature. Who knows, you might just avoid becoming part of the story yourself.
Call to Action
Now that you know all about lightning scars, why not share this article with your friends and family? Knowledge is power, and the more people know about the dangers of lightning, the safer we all will be. And if you have any questions or comments, feel free to leave them below—I’d love to hear from you!
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Is a Lightning Scar?
- How Do Lightning Scars Form on Trees?
- Lightning Scars on Humans: A Rare but Powerful Encounter
- The Science Behind Lightning Scars
- Factors That Influence Lightning Scar Formation
- Preventing Lightning Scars: Safety Tips and Strategies
- Lightning Protection Systems: How They Work
- The Environmental Impact of Lightning Scars